Since August 2017 the Masai Farm in Olpirikata, Kenia is up and running and already after five months it has turned autonomous and the ten men working on the farm can be paid with proceeds of the milk sale.
Chicken are also raised on the farm and this connects to one of our future projects, which we will present soon. On the occasion of the upcoming easter celebrations, we have collected a couple of facts about eggs.
Happy reading!
How many eggs does a chicken lay ?
A hen lays approximately up to 280 eggs a year. The amount may vary due to the breed and age of a chicken as well as their feed and environment. They do not lay eggs during the molting season which is when they shed their old old feathers and grow new feathers.
What determines the color of egg shells?
The color of a hen’s egg shells is determined genetically and is not influenced by the feathers or the feed – actually it is determined by their ears. Or more precisely , the color of a hen’s egg shells is determined by the color of the patches where their earlobe would be. Hens with white patches lay white eggs and hens with red patches produce brown eggs. Moreover, there are some breeds known for blue or green eggs. These breeds also have red patches.
How does the color get into the egg shell?
The different colors of egg shells come from the storage of color pigments in the egg shell which is made of calcium carbonate, a crystal white in color. Consequently, white eggs do not have any pigment in their shell.1) The blue-green color of eggs shells, named oocyan, is considered to consist, in part, of the bile pigment biliverdin. 2)
The color of the eggs is established in the egg gland of the hen where color pigments produced priorily as a side product of blood and bile (where they are stored) are being brought to the calcium shell. If all color pigments come together the color of the egg shell will be brown. If a hen lacks the gene for color production her eggs will be white.
The color of an egg shell, however, does not influence the taste or the nutritional value of an egg. Feeding, environment and genetics are responsable for these characteristics.
Why is the egg not round?
A raw egg is not as fragile as it appears. Even though the egg shell measures only 0.4 mm in thickness, it is almost impossible to break an egg kept upright between the fingers of a hand and even when it is lying flat it is almost impossible to break it with the fingers. The explanation for this resistence can be found in its curved shape, which evenly distributes the pressure applied on one spot over the curve. And of course, the egg has to resist the weight of the hatching hen.
The stability of the curved form also applies to a spherical form. The reason why nature opted for a different packing design is the different rolling pattern once an egg falls out of nest – a spherical shaped egg would roll away much easier than a normal shaped egg. 3) This can be tried out easily: Put a ball and an egg on a table and push them. The ball will roll much longer and maybe even fall off the table whereas the egg will make a curve and roll in a much more irregular way.
What is the nutritional value of an egg?
Eggs are among the most precious animal foods. The biological valence of eggs is higher than that of fish, meat and milk. The egg protein helps the human body to develop important proteins for different body functions and furthermore provides energy and is essential for the composition of muscles.
The yolk is rich in vitamins (A, D, K, B12), protein, calcium, iron as well as fat and cholesterol. The yolk represents on average 42% of an egg’s weight.
An egg white is made mainly of a protein called albumen, and also contains niacin (vitamin B3), riboflavin (vitamin B2), chlorine, magnesium, potassium, sodium and sulfur, according to the Iowa Egg Council, an industry group. The white contains about 58 percent of an egg’s protein.
The so called chalazae are two spiral bands of tissue that suspend the yolk in the center of white and thus prevent the yolk’s attaching to the shell. Fresh eggs show a higher viscosity of the egg white compared to older eggs. The egg white represents on average 58% of the weight of an egg. 5)
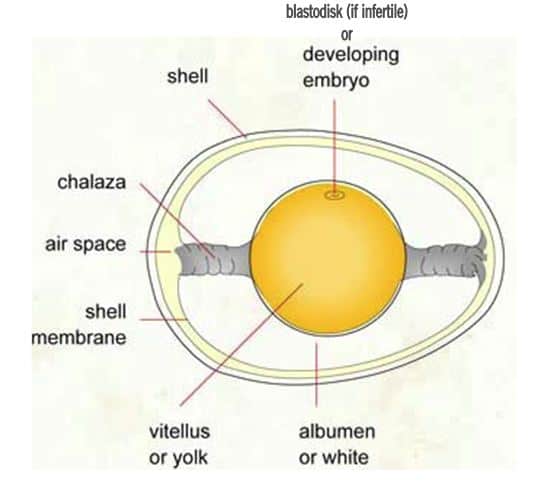
The Egg Anatomy of the University of Kentucky Source: http://www.the-chicken-chick.com/2012/09/hatch-along-with-chicken-chick-part-3/egg-anatomy-from-univ-of-kentucky/
How long do eggs last?
Fresh eggs have a minimum shelf life of 28 days after laying. But even after the expiry date they sometimes stay fresh past that date and they do not have to be tossed yet. Old eggs should be heated to at least 70 degrees centigrade to make them safe for consumption.
How to test the freshness of eggs:
The water and bowl test
Place the eggs in a bowl of water. If the egg lays on its side at the bottom, it is still quite fresh. If the egg stands upright on the bottom, it is still fine to eat, but should be eaten very soon, or hard-boiled. If the egg floats to the top, it is past its prime, and not good for eating.
The cracked egg and plate test
The yolk of a fresh egg will have a round and compact appearance and it will sit positioned quite high up in the middle of the egg. The white that surrounds it will be thick and stay close to the yolk. A cloudy coloring to the egg white is a sign of extra freshness, as this « cloudiness » is in fact carbon dioxide, which is present when the egg is laid. Over time, the egg white will become more transparent, as the carbon dioxide dissipates. A less fresh egg will contain a flatter yolk that may break easily and a thinner white that spreads quite far over the plate.
The sound test
Gently shake the egg from side to side. If you cannot hear any sound whatsoever, the egg is perfectly fine to eat and there is nothing wrong with it.
How to store eggs?
Fresh eggs do not have to be stored in the fridge – unless the eggs have been bought stored in the fridge at the supermarket. Consequently, the cold chain should not be broken and the eggs should be stored in the fridge as cold eggs do cope very badly with a change in temperature. An increase in temperature provokes the water condensation on the shell which will damage the cuticle. Thus, germs may get into the inside of the egg. Storing the eggs in the fridge protects the vitamins in the egg from light and oxygen.
So whether or not your store the eggs in the fridge depends on how they were when you bought them but it is very important to protect them from light exposure – in or out of the fridge. Also do they have to be stored with their rounder side up, as storing them upside down would cause the air space to move and cracking the shell membrane which would increase the possibility of bacteria entering.
Why can you store eggs outside the fridge ?
The shell is equipped with approximately 10.000 pores providing the calcium crystals of the shell with a grid like structure which function as a respirational system. The shell is covered with a thin strata, the so called cuticle, that prevents germs from accessing the inside of the egg. Water destroys this natural protection sheet of the egg. Therefore: never wash an egg before storage. 4)
Tips and tricks for handling eggs
- Store them best in a carton, protected from light and oxygen.
- Never expose fresh eggs to the sun.
- Extreme changes in temperature negatively impact the natural protection of the egg, deteriorates the quality and accelerates the aging process of an egg.
- You can use eggs after their shelf line date provided that they do not smell badly. At that age though it is safer to not eat them heated at least to 70 degrees centigrade either in a cake or boiled or hard boiled.
- Cooking them at a temperature above 90 degrees centigrade can provoke a chemical reaction between the iron of the yolk and the sulfur of the egg white which may lead to the creation of a green ring around the yolk. Putting the egg into cold water after cooking may prevent this.
- Eggs are best to eat from day four after laying as it still has to fully develop after being laid.
- Always store eggs with the rounder side up to prevent the movement of the air space within the egg. 6)
- Never wash eggs before storing them – washing destroys their natural protective layer.
- Do not store eggs close to smelly food.
- Hard boiled eggs from somewhat older eggs can be peeled easier as the older egg has already changed its acidity due to loss of carbon dioxide through the shell. 7)
- Do not chill hard boiled eggs after cooking as this reduces their expiry date. Hard boiled eggs can be stored four weeks and in the fridge up to six weeks.
- Remnants of yolk and egg white can be frozen or kept in a small glass. Add some sunflower oil or cold water to prevent it from drying out and put it into the fridge.
- Egg shells can be used as fertilizer or be composted.
Sources
- http://www.wirkochen.at/lexikon/Der-Unterschied-zwischen-braunen-und-weissen-Eiern/240782411
- Wikipedia : https://en.wiktionary.org/wiki/oocyan
- http://www.daserste.de/information/wissen-kultur/w-wie-wissen/sendung/2010/die-perfekte-form-ei-100.html
- https://www.focus.de/gesundheit/praxistipps/eier-richtig-lagern-darauf-kommt-es-an_id_6931486.html.
- https://www.lebensmittellexikon.de/e0000520.php
- www.eier.de
- Zitiert nach Thomas Vilgis, Forscher am Max-Planck-Institut für Polymerforschung in Mainz und Experte unter anderem für die Physik von Nahrungsmitteln im Artikel «Warum sich manches Ei schwer pellen lässt» vom 08.04.2012



